Token Economy
Abstract
In a blockchain network, the token economy can be classified into different archetypes. This makes it possible to assign a token to a specific use case.
Motivation
If you come to the conclusion that you want to use tokens, the question naturally arises as to which tokens you can use for which use case. There are a variety of ways to use tokens in a blockchain network. Whether as a reward or as a voting mechanism in which the authorised persons are clearly identifiable. Many things can be realised with tokens. Tokens also provide time-contingent rewards for behaviour. This makes the blockchain network much more effective and efficient to use according to the desired type of use. By creating such values, the effect is also amplified. Therefore, the operation itself becomes more attractive for the members of the consortium.
Elaboration
To facilitate the decision-making process, a list of all defined token archetypes is provided below. This list was taken from the paper "To Token or not to Token: Tools for Understanding Blockchain Tokens" Oliveira et al - 2018.
| Archetype | Main Purposes |
Description |
|---|---|---|
| Crypto- Currency (Crypto- Currencies) |
Currency | A token with the ambition to become a widespread digital form of currency. |
| Equity Token (Tokenised Securities) |
Earnings, Store of Wealth |
A token which confers to its holder a right to equity-related earnings, such as profitsharing, application rents or platform fees. |
| Funding Token (Utility Tokens) |
Store of Wealth, Funding |
A token which is perceived as a long-term investment from the holder’s perspective, and as a financing vehicle for the project’s team and/or the community (bounties). |
| Consensus Token (Utility Tokens) |
Validation Reward, Store-of- Wealth |
A token which is used as a reward to nodes which ensure data validation and consensus. |
| Work Token (Utility Tokens) |
Work Reward |
A token which is used as reward to users who complete certain actions or exhibit certain behaviour. |
| Voting Token (Utility Tokens) |
Voting Right |
A token which confers a voting right to its holder. |
| Asset Token (Utility Tokens) |
Voting Right, Asset Ownership |
A token which represents asset ownership. |
| Payment Token (Utility Tokens) |
Payment | A token which is used as internal payment method in the application. |
In the same paper "To Token or not to Token: Tools for Understanding Blockchain Tokens" Oliveira et al. - 2018, a decision tree was developed to identify as easily as possible those tokens that are needed for the corresponding use case. As there is a constant evolution of the token economy, further research is recommended. The following image was taken from the paper. These give a good indication whether one needs a token and which archetype it would be accordingly. If you can answer the questions with the exception of the last one with "yes", a token is recommendable and very likely the right instrument for the application.
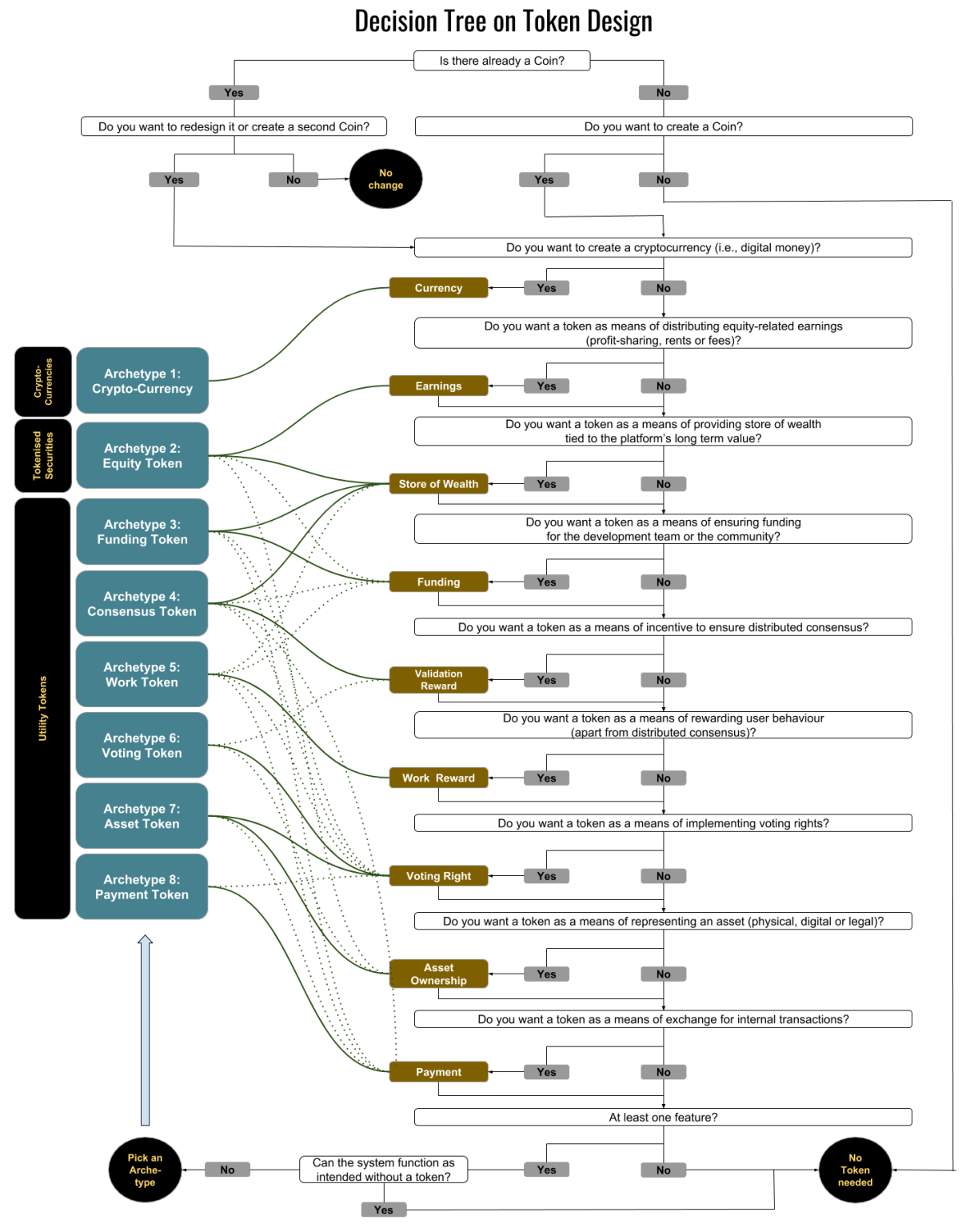
This process makes it very easy to obtain the required tokens for the blockchain network. Since there are many use cases and the blockchain network can be very individually designed, the tokens must of course be individually adapted to the respective system.
Internal references and dependencies
(Lists of internal references and dependencies)
References to best practice, examples
(List of references to best practice, examples)
Bibliography of selected references
Oliveira, Luis, Liudmila Zavolokina, Ingrid Bauer, and Gerhard Schwabe. 2018. ‘To Token or Not to Token: Tools for Understanding Blockchain Tokens’. In Oliveira, Luis; Zavolokina, Liudmila; Bauer, Ingrid; Schwabe, Gerhard (2018). To Token or Not to Token: Tools for Understanding Blockchain Tokens. In: International Conference of Information Systems (ICIS 2018), San Francisco, USA, 12 Dezember 2018 - 16 Dezember 2018. San Francisco, USA: s.n. https://doi.org/10.5167/uzh-157908.
RFC-0721
Contributing authors: David Maas
Status of this document: work in progress
Last day modified: 2021-06-08